The road to a circular future: this is how Recticel is tackling it

Fundamentally sustainable
Recticel Insulation is fully embracing sustainability and circularity. Not just hot air, Recticel suggests how to do it in six concrete steps. "If we really want to move towards a circular future, we need to ensure the actions we take are concrete."
"Sustainability is a broad concept, which you have to approach in different ways," explains Dirk Vermeulen, Head of Technical Management at Recticel Insulation. "On the one hand, it's about climate action, CO2 reduction in terms of the three different scopes and circularity, but sustainability is also in personnel management and the human aspect."
Recticel has been working on its sustainability strategy for some time, but now wants to position itself clearly. "We want to commit ourselves as a circular construction partner," Dirk continues. "The latter is a challenge in a traditional sector like construction, we need partners as part of this process."
Watch the Dutch version here
To map and deepen the process, Recticel formulated six steps:
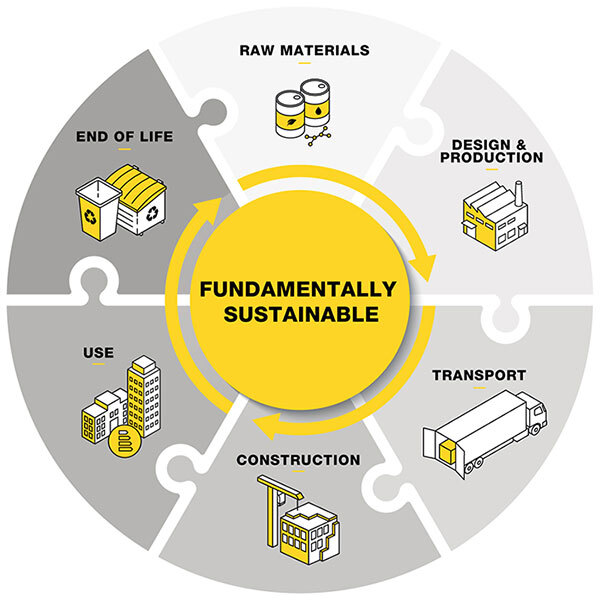
1. Raw materials
It all starts and ends with the raw materials used to make insulation. "In an ideal world, insulation is made entirely of 'ecological' materials - either of organic or recycled origin. However, reality tells us that we do not necessarily achieve the same performance and quality," Dirk explains. Recticel is committed to these two avenues: replacing basic raw materials with organic alternatives on the one hand, and striving for circularity by using recycled raw materials on the other. For example, Eurothane Silver Impact, a thermal insulation board for flat roof applications, uses raw materials that already consist of 25% biocircular material (determined by the mass balance method).
A second example is the 'Sweetwoods' project where the aim is to replace a number of the polyols, which come from fossil fuels, in our insulation with, for example, lignin, a substance from sustainable hardwood."
For the raw materials that Recticel wants to make as circular as possible, the company is working with research institutions such as KU Leuven as well as other raw material suppliers to scrutinise and develop the (chemical) processes needed to do so.
So, to ensure that we have enough raw materials of sustainable origin, we need raw materials of biological origin as well as circular raw materials (from recycling).
2. Design & production
Recticel are working on several fronts in the next stage of the process being the design and production phase. "One of the important elements during production, is energy," says Dirk. "We aim to be energy-neutral, including in our production. That means being energy efficient on the one hand and as green as possible on the other."
But manufacturing is also about waste and reducing it. "We design and manufacture our products as efficiently as possible to minimise production waste. What does end up in our waste stream goes as raw material to other companies that reuse it to produce insulating construction boards."
3. Transport
Dirk: "Once our goods are ready, they obviously need to be transported to the construction site. We work together with our transport partners to optimise transport as much as possible, for example by loading the trucks to the maximum."
4. Construction
On the construction site, Recticel has no direct influence on the amount of (cutting) waste generated. However, we want to be smart about this waste problem on sites. "While installing insulation, some material is always lost. We do try to reduce that cutting waste with smart design, among other things. In our search for solutions, we are working with several partners who will support us in waste collection in Belgium and France. In all other countries, this track is being further explored with local partners.
5. Use
Everyone has to get involved for it to succeed, that much is clear. "That also applies to building owners and developers," notes Dirk. During the use phase of buildings, it is obvious that we should all strive to keep energy consumption as low as possible.
Recticel is already doing its bit: "We make our insulation material so that it can last throughout the life of the building and have a significant impact on reducing the CO2 emissions of the building it insulates during the use phase. So our products are sustainable in themselves, in the sense that they do not require replacement during a building's normal lifetime. Yet another waste stream avoided."
6. End of life
Everything comes together in the final step: "At the end of the cycle, we want to return to the beginning again and reuse the materials and raw materials. Ecodesign, where all building elements such as the insulation boards become possible to retrofit, is important to us.
Indeed, the insulation could possibly be reused afterwards, provided a check of its key properties is undertaken.
In addition, we want to fully commit to researching recycling solutions so that PIR could be converted back into a basic raw material. As a result, we are currently looking into this, together with the industry, to understand possible techniques such as pyrolysis and chemolysis to make that possible."
Clear objectives
The bar is high, it is clear. "The European Union has already set high expectations and standards with the Green Deal. We impose targets on ourselves, to set out the path. Everyone says they are working on sustainability, but you have to make it concrete. Otherwise, you are selling hot air."
"Moving forward you have to look into the future: if we want to change something, we should not only set up concrete actions, but also communicate about what we are doing as well as involve others. We won't get there alone."
Latest insights & stories

A Global Movement: The World Unites in a Pink Pledge for Clean and Sustainable Water
5,000 participants. 32 countries. €30,000 funds raised. And that's just the beginning.
Picture this: One step that sends ripples across the globe, transforming lives and creating waves of change. You might wonder, how can such a simple action for most of us have such a profound impact?

Sustainability and circularity in construction
Join us in transforming the future of construction, creating buildings that not only stand the test of time but also contribute to a healthier planet!

RainTunes: Shower scenarios for the soul
Light, hearing, smell, and touch: Together with experts, we have developed sensuous scenarios that turn showering into an individual experience. Whether you want to prepare for the day ahead or relax after working out. Whether you want to refresh after a day’s work or unwind at the end of the evening: RainTunes surprises with multisensory experiences.*
*Currently available only in Germany and Austria.